What are Data Centers

Data centers are specialized facilities designed to operate as centralized facilities that house computer systems and associated components, such as telecommunications and storage systems. Their primary function is to store, manage, and disseminate data and applications for businesses, cloud service and online applications. Here’s an overview of how data centers operate:
- Infrastructure: Data centers consist of physical infrastructure including servers, storage devices, networking equipment, power supplies, cooling systems, and security devices. These components work together to ensure continuous operation.
- Servers: Servers are powerful computers that process data and run applications. They are organized in racks and connected through high-speed networks to communicate internally and externally.
- Networking: Data centers use complex networking technologies to connect servers within the facility and link to external networks, such as the internet. This includes routers, switches, firewalls, and load balancers to manage data traffic efficiently and securely.
- Power and Cooling: Data centers require a constant and reliable power supply, often supported by backup generators and uninterruptible power supplies (UPS). Cooling systems prevent overheating of equipment, using methods like air conditioning, liquid cooling, or advanced airflow management.
- Security: Physical security measures include surveillance cameras, biometric access controls, and security personnel to prevent unauthorized access. Cybersecurity measures protect against data breaches, malware, and other digital threats.
- Data Management: Data centers manage data storage, backup, and recovery processes to ensure data integrity and availability. They often use redundant systems and data replication to prevent data loss.
- Monitoring and Maintenance: Continuous monitoring of hardware and software ensures optimal performance and early detection of issues. Regular maintenance and updates help maintain reliability and security.
- Scalability and Redundancy: Data centers are designed to scale resources up or down based on demand. Redundant systems and failover mechanisms ensure high availability and minimize downtime.

In summary, data centers operate through a combination of robust infrastructure, advanced technology, and stringent management practices to provide reliable, secure, and efficient data services.
Data Centers Impact on the Environment and Communities

Environmental Impact:
- Energy Consumption: Data centers consume vast amounts of electricity to power servers and cooling systems. This high energy demand often relies on fossil fuels, contributing to carbon emissions and climate change.
- Water Usage: Cooling systems in data centers require substantial water resources, which can strain local water supplies, especially in arid regions.
- Electronic Waste: The rapid turnover of hardware generates electronic waste, which, if not properly recycled, can lead to environmental contamination.
- Land Use: Construction of data centers can lead to habitat disruption and land use changes.
Impact on Communities:
- Economic Benefits: Data centers can bring jobs and infrastructure improvements to local communities.
- Resource Competition: High water and energy use may compete with local needs, affecting residents and businesses.
- Noise and Traffic: Construction and operation can increase noise levels and traffic congestion.
- Social Equity: The benefits and burdens of data centers may not be evenly distributed, potentially impacting vulnerable communities disproportionately.
Mitigation Strategies:
- Adoption of renewable energy sources to reduce carbon footprint.
- Implementation of water-efficient cooling technologies.
- Responsible e-waste management and recycling programs.
- Community engagement to address concerns and share benefits.
Understanding and managing the environmental and community impacts of data centers is essential for sustainable digital infrastructure development.
Are Data Centers Safe
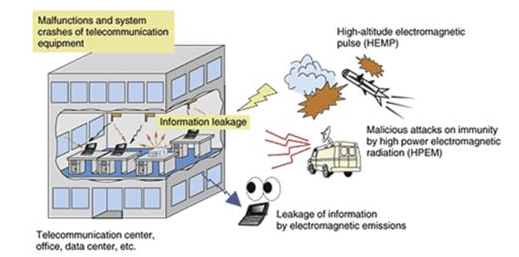
Data centers are generally considered safe for people living near them. They are designed with strict safety standards and regulations to minimize any risks. The main concerns people might have include electromagnetic radiation, noise, and environmental impact.
- Electromagnetic Radiation: Data centers use a lot of electrical equipment, but the levels of electromagnetic fields (EMF) they emit are typically well below international safety limits set by organizations like the World Health Organization (WHO).
- Noise: Data centers have cooling systems and backup generators that can produce noise. However, they are usually located in industrial areas or designed with soundproofing to minimize noise pollution affecting nearby residents.
- Environmental Impact: Data centers consume significant energy, which can have environmental implications. Many modern data centers use energy-efficient technologies and renewable energy sources to reduce their carbon footprint.
Overall, living near a data center does not pose significant health risks, but it’s always good to check local regulations and any community reports related to specific facilities.
Pros and Cons of Data Centers Near You
Pros:
- Economic benefits: Data centers can create jobs and boost local economies.
- Infrastructure improvements: They may lead to better power grids and internet connectivity.
- Technological advancement: Proximity to data centers can attract tech companies and innovation.
Cons:
- Environmental impact: Data centers consume significant energy and water resources, potentially affecting local ecosystems.
- Noise and traffic: Construction and operation may increase noise and traffic in your area.
- Property values: Some people worry data centers might affect property values negatively.
Ultimately, your stance should depend on how these factors align with your community’s values and priorities. Engaging with local planning processes and understanding the specific data center project can help you make an informed decision.

Leave a Reply